- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Bengali
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- French
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- Miao
- Hungarian
- igbo
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Feb . 10, 2025 22:57 Back to list
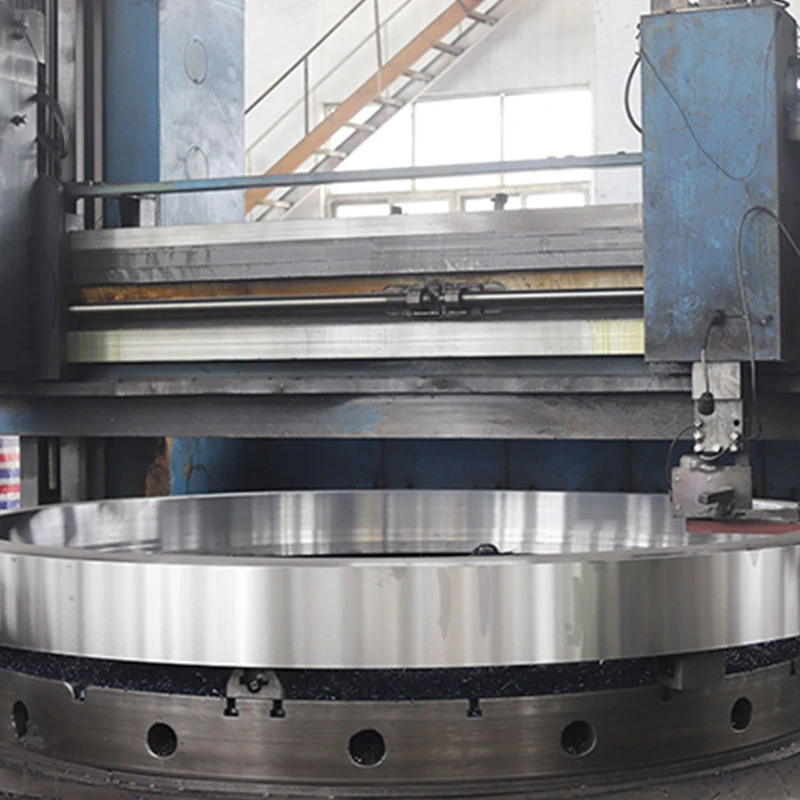
Roll Hoops
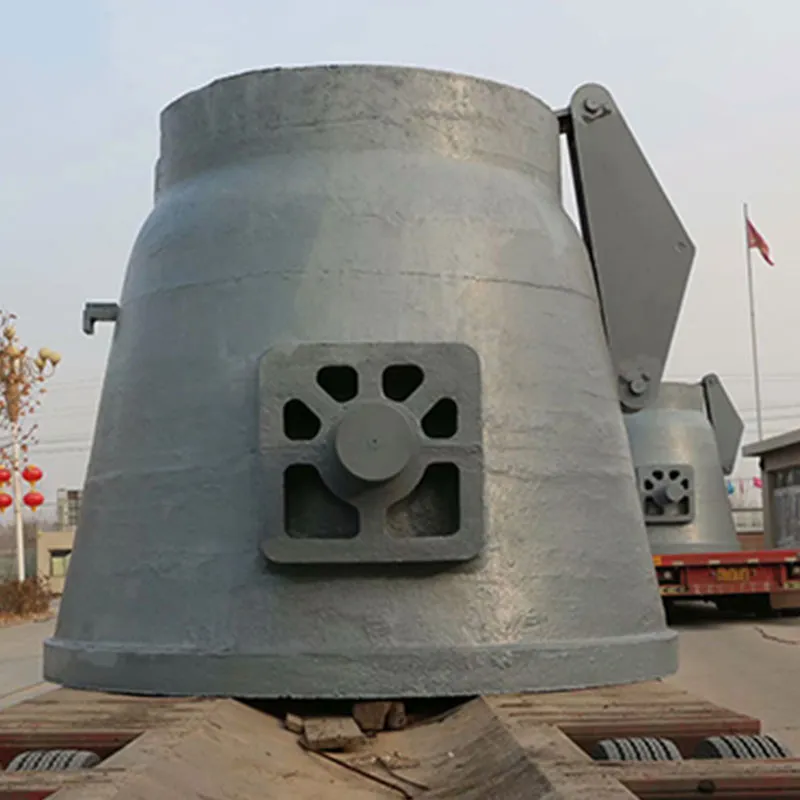
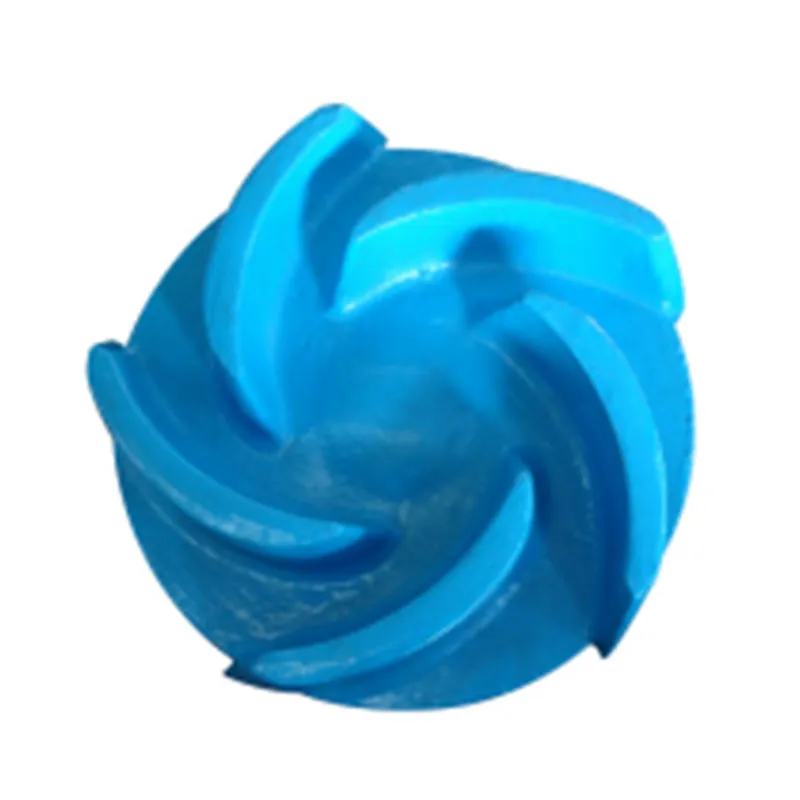


In terms of practical application, engineers often leverage advanced simulation tools such as Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) to predict the performance of slag pump designs before physical prototypes are constructed. These tools offer insights into potential challenges and enable the optimization of designs in the early stages, reducing the risks and costs associated with trial-and-error testing. Further credibility is achieved through continuous innovation, where insights from the latest technological advancements, such as the integration of IoT for predictive maintenance and automated controls for optimal performance, are applied. Implementing real-time monitoring systems can alert operators to deviations from expected performance, thereby reducing unexpected failures and maintenance costs. To foster industry trust, effective communication about the benefits and unique features of a slag pump design can be facilitated through white papers, webinars, and seminars. These platforms not only inform but also involve stakeholders in the design process, thus fostering a sense of reliability and openness. Ultimately, the design calculation of a slag pump is a multidisciplinary task that necessitates a high level of technical skill, attention to detail, and adherence to industry standards. Manufacturers who prioritize these aspects not only enhance their products but also solidify their position as leaders in the industry, providing pumps that are both efficient and enduring. By focusing on these key areas, companies can develop slag pumps that meet the rigorous demands of industrial environments, thus securing their reputation as reputable and trustworthy providers.
-
Low-Cost Borehole Drilling Machine for Small-Scale Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Carbide Bullet Teeth for Abrasive Formations: Powering Industrial Drilling Efficiency
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Advantages of Down-the-Hole Drill Bits in Geothermal Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Hole Hammer Use in Water Well Drilling
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of a Mobile Diesel Compressor in Construction
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Diesel Portable Screw Air Compressors
NewsJul.11,2025