- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Bengali
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- French
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- Miao
- Hungarian
- igbo
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Feb . 20, 2025 02:31 Back to list
tipo de eje de bomba

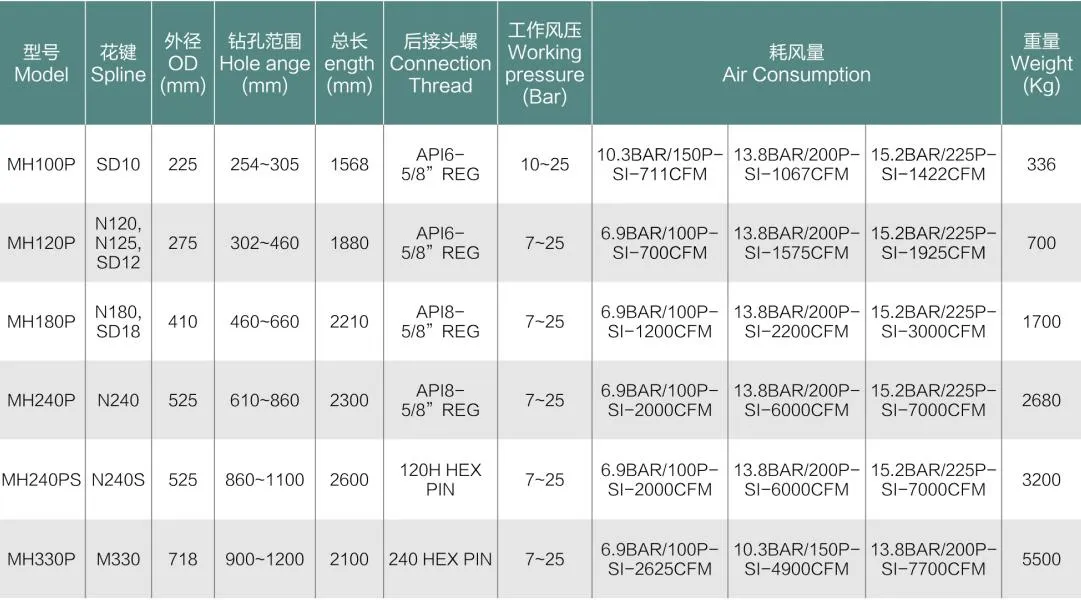
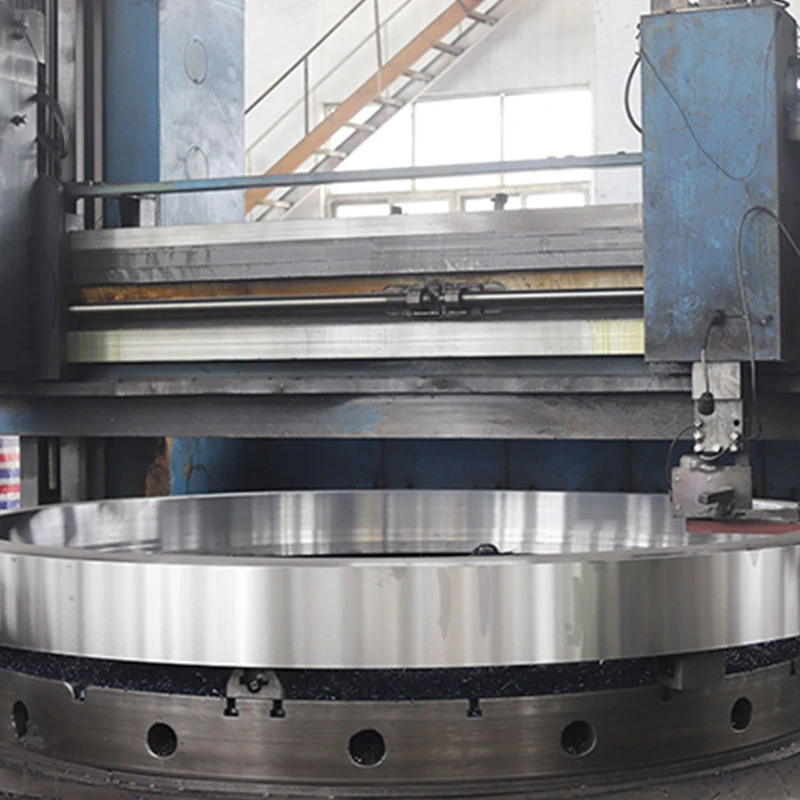
4. Splined Shafts For applications demanding high torque and precise movement, splined shafts are often utilized. These shafts feature a series of ridges or teeth that align with mating components, ensuring a strong torque transfer with minimal slip. Splined shafts are common in industrial settings where precision and high performance are required, such as in manufacturing pumps for precision-machined parts or components. 5. Tapered Shafts Frequently used in applications where space is at a premium, tapered shafts offer the advantage of easy assembly and disassembly. The taper in the shaft design helps in securing components tightly while facilitating easy alignment. These shafts are ideal when frequent maintenance or component swaps are necessary, reducing downtime and labor costs. Choosing the correct type of pump shaft involves more than just assessing the immediate needs of the system. It requires an in-depth understanding of the operational environment and the specific demands placed on the pump. Characteristics such as load, rotational speed, environmental factors, and maintenance requirements all play pivotal roles in the selection process. Consulting with a professional who has expertise in pump systems can provide invaluable insights and help avoid common pitfalls associated with incorrect shaft selection. In conclusion, the type of pump shaft chosen can significantly affect the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of a pump system. By understanding the distinct features and applications of each shaft type, you can make informed decisions that align with the specific requirements of both the project and the operational environment. Trust in expertise and experience when navigating these choices, as the right selection can lead to significant gains in performance and cost savings over time.
-
Low-Cost Borehole Drilling Machine for Small-Scale Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Carbide Bullet Teeth for Abrasive Formations: Powering Industrial Drilling Efficiency
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Advantages of Down-the-Hole Drill Bits in Geothermal Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Hole Hammer Use in Water Well Drilling
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of a Mobile Diesel Compressor in Construction
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Diesel Portable Screw Air Compressors
NewsJul.11,2025