- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Bengali
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- French
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- Miao
- Hungarian
- igbo
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Feb . 20, 2025 01:33 Back to list
selección del material del eje de la bomba
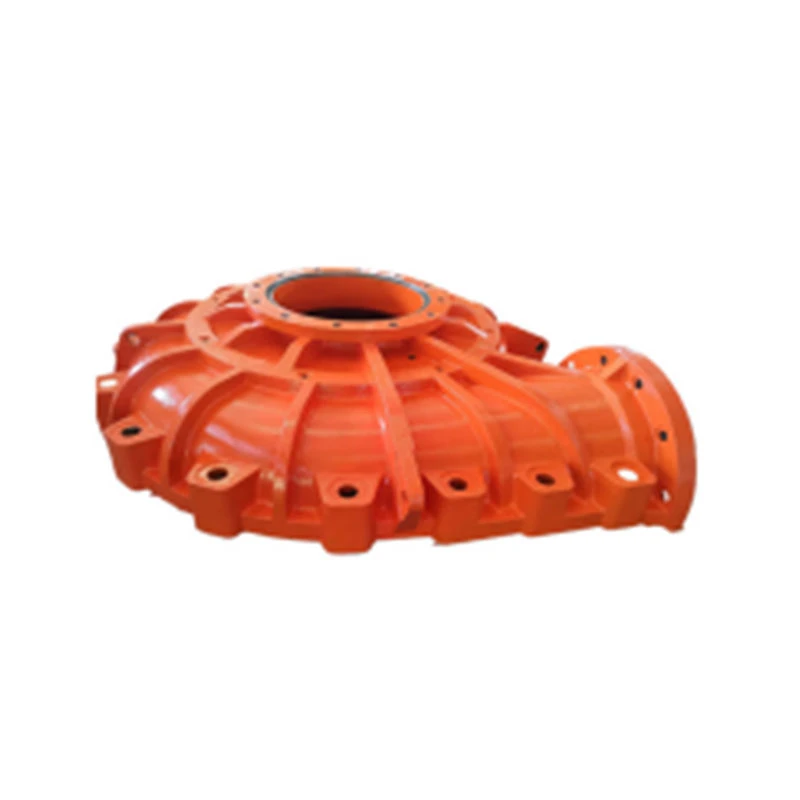


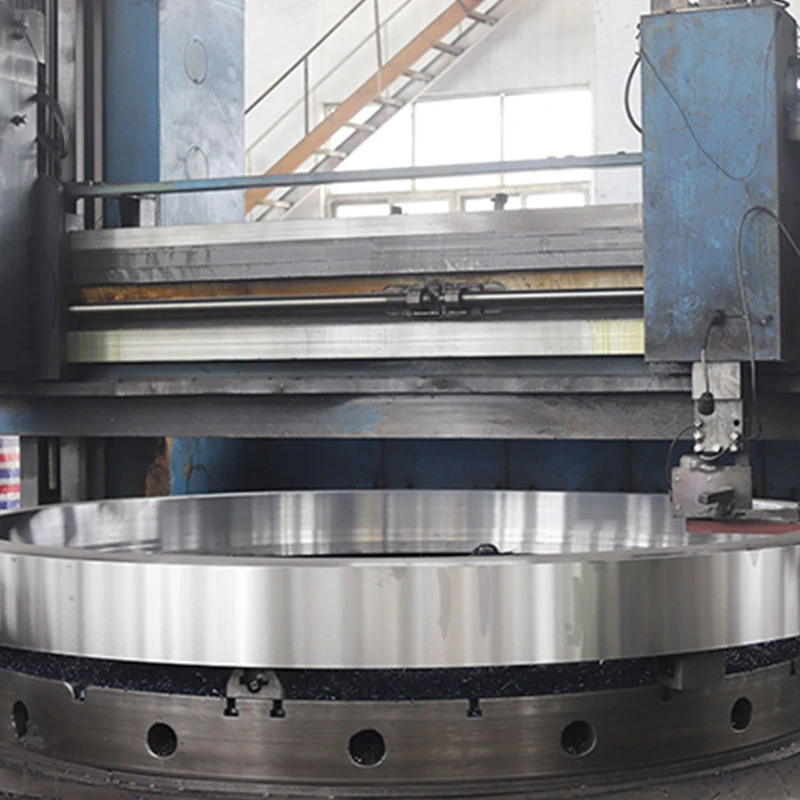
Thermal expansion, galling, and electrical conductivity also influence the material choice for pump shafts. For instance, in high-temperature applications, materials with greater coefficients of thermal expansion may lead to misalignments or failure if not accounted for in the design phase. Similarly, galling—a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces—can be mitigated by selecting materials with suitable hardness ratios. To enhance performance further, surface treatments and coatings like nitriding, carburizing, or applying specialized polymer coatings can be employed. These treatments improve surface hardness and wear resistance, prolonging the shaft's lifecycle. Selecting the right treatment depends on the specific wear conditions the pump will face. In applications where precision and smooth operation are paramount, such as in medical or food processing industries, the material's ability to undergo micro-finishing processes is a consideration. The smoother the shaft surface, the less likely it is to harbor bacteria or impede the operation of closely toleranced components. Furthermore, environmental considerations play an increasingly vital role in material selection. Opting for recyclable materials or those produced through sustainable methods can enhance a company’s environmental credentials, providing a competitive edge in markets that prioritize sustainability. In summary, selecting the appropriate material for a pump shaft involves balancing mechanical and environmental conditions with cost and sustainability considerations. It requires an in-depth understanding of the operational environment and the specific demands placed upon the pump system. By aligning material selection with these considerations, businesses can ensure longevity, reliability, and safety, ultimately contributing to reduced maintenance costs and downtime.
-
Low-Cost Borehole Drilling Machine for Small-Scale Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Carbide Bullet Teeth for Abrasive Formations: Powering Industrial Drilling Efficiency
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Advantages of Down-the-Hole Drill Bits in Geothermal Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Hole Hammer Use in Water Well Drilling
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of a Mobile Diesel Compressor in Construction
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Diesel Portable Screw Air Compressors
NewsJul.11,2025