- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Bengali
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- French
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- Miao
- Hungarian
- igbo
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Feb . 14, 2025 09:27 Back to list
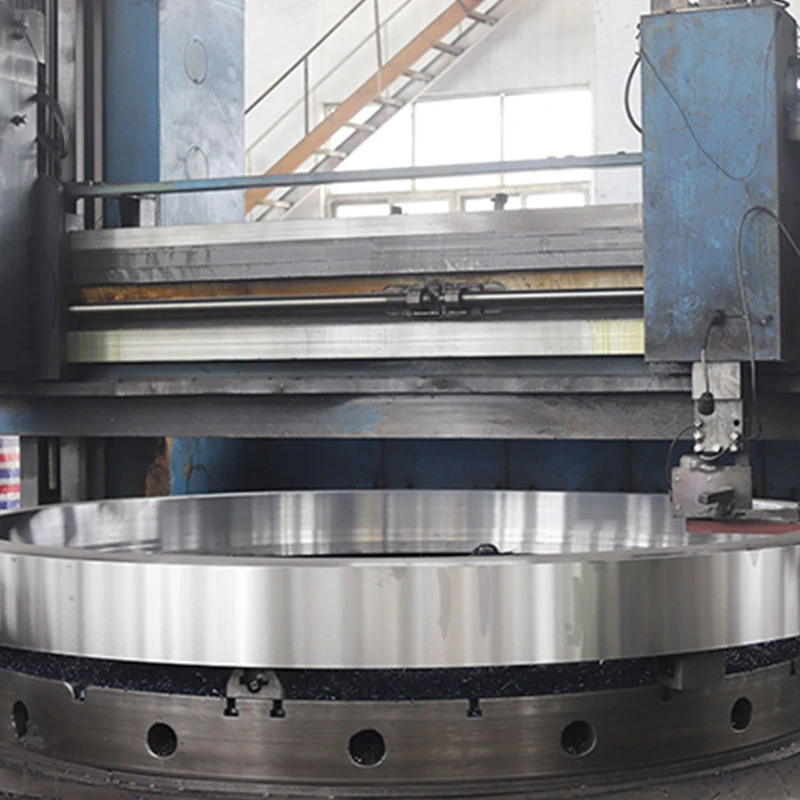
materiales de placa de titanio


Beyond mechanical properties, the marketability of titanium plates owes much to their surface characteristics. These plates offer a range of finishes, from polished to acid-etched, granting architects and designers creative freedom. Whether it's the sleek facades of modern skyscrapers or intricate installations in art galleries, titanium plates provide a blend of durability and aesthetic appeal unmatched by traditional materials. The cost factor, often a primary concern, is offset by titanium's longevity and minimal maintenance requirements. Unlike materials prone to corrosion or wear, titanium's resilience against environmental factors extends its lifecycle, translating to long-term savings and reliability. This cost-benefit analysis is crucial for sectors where operational integrity is paramount, such as offshore oil rigs or chemical processing plants. Moreover, the sustainable aspect of titanium cannot be overlooked. As industries strive toward eco-friendly practices, titanium's recyclability ensures it meets modern environmental standards. Engineers and manufacturers are able to integrate titanium plates into projects without compromising on ecological commitments, a significant draw in today's climate-conscious market. Real-world applications further cement titanium's status. The aerospace industry, constantly pushing the boundaries of innovation, relies on titanium plates for components such as wing structures and engine parts where weight reduction and performance are critical. In medical fields, titanium's non-toxic characteristics ensure it remains a staple for devices that necessitate both precision and patient safety. In conclusion, the exploration of titanium plate materials should be guided by a comprehensive understanding of their properties, applications, and intrinsic benefits. By leveraging the expertise surrounding titanium, industries can adopt these plates not just as materials but as integral solutions to complex challenges. Trust in titanium's capabilities and the authoritative insight behind its use can lead to enhanced project outcomes, reinforcing its position as an indispensable asset across multiple domains.
-
Low-Cost Borehole Drilling Machine for Small-Scale Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Carbide Bullet Teeth for Abrasive Formations: Powering Industrial Drilling Efficiency
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Advantages of Down-the-Hole Drill Bits in Geothermal Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Hole Hammer Use in Water Well Drilling
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of a Mobile Diesel Compressor in Construction
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Diesel Portable Screw Air Compressors
NewsJul.11,2025