- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Bengali
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- French
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- Miao
- Hungarian
- igbo
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Feb . 19, 2025 12:01 Back to list
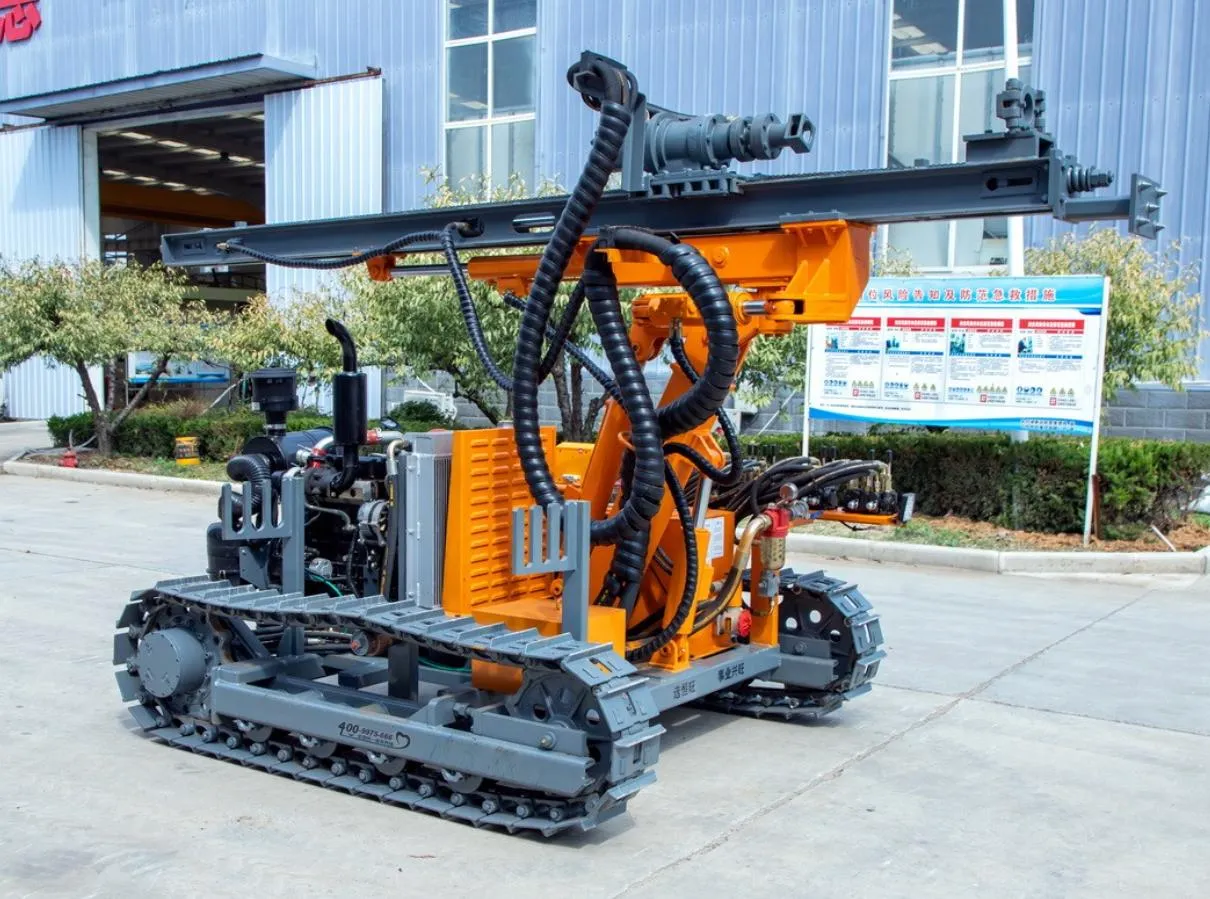
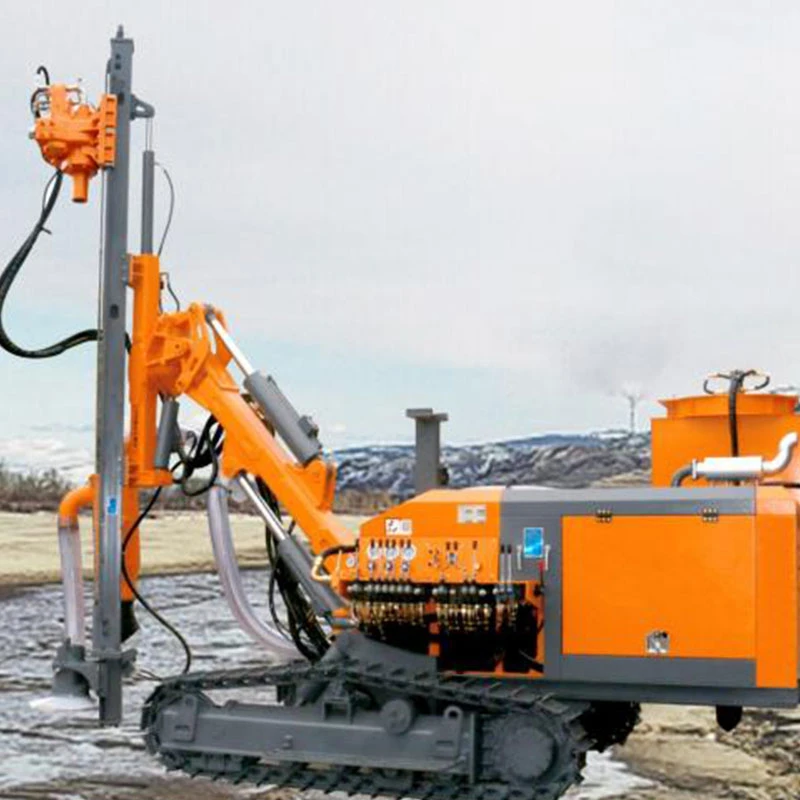
Integrated Surface DTH Drilling Rig


For applications demanding high performance and lightweight properties, titanium comes into play. Its low density coupled with high strength makes it ideal for pumps used in specialized industries such as aerospace. Titanium's resistance to both corrosion and extreme temperatures often outweighs its higher cost, making it a long-term investment in environments where these factors are prevalent. Each material choice affects the water pump shaft's lifecycle, maintenance needs, and suitability for specific applications. Expert design considerations involve not just the material but also understanding the environmental conditions and operational requirements of the pump. For instance, while stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, it might not be necessary for all applications, leading to unnecessarily increased costs. Conversely, opting for a material like brass or bronze could reduce initial costs but might not meet lifespan expectations under certain conditions. When selecting a material for a water pump shaft, consulting with industry experts ensures a balance between cost-effectiveness and performance. Leveraging advanced computational models and real-world testing can provide authoritative insights into how different materials perform under specific conditions. Customizing the shaft material based on precise operational data enhances trustworthiness and reliability over the pump's operational life. In conclusion, the choice of water pump shaft material requires a blend of experience, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness. With continuous advancements in material science technology, the landscape of possible materials is expanding. By considering the unique performance attributes of each material and aligning them with the operational demands of the water pump, more effective and efficient fluid handling solutions can be achieved.
-
Low-Cost Borehole Drilling Machine for Small-Scale Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Carbide Bullet Teeth for Abrasive Formations: Powering Industrial Drilling Efficiency
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Advantages of Down-the-Hole Drill Bits in Geothermal Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Hole Hammer Use in Water Well Drilling
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of a Mobile Diesel Compressor in Construction
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Diesel Portable Screw Air Compressors
NewsJul.11,2025