- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Bengali
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- French
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- Miao
- Hungarian
- igbo
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Feb . 19, 2025 10:53 Back to list
Impeller
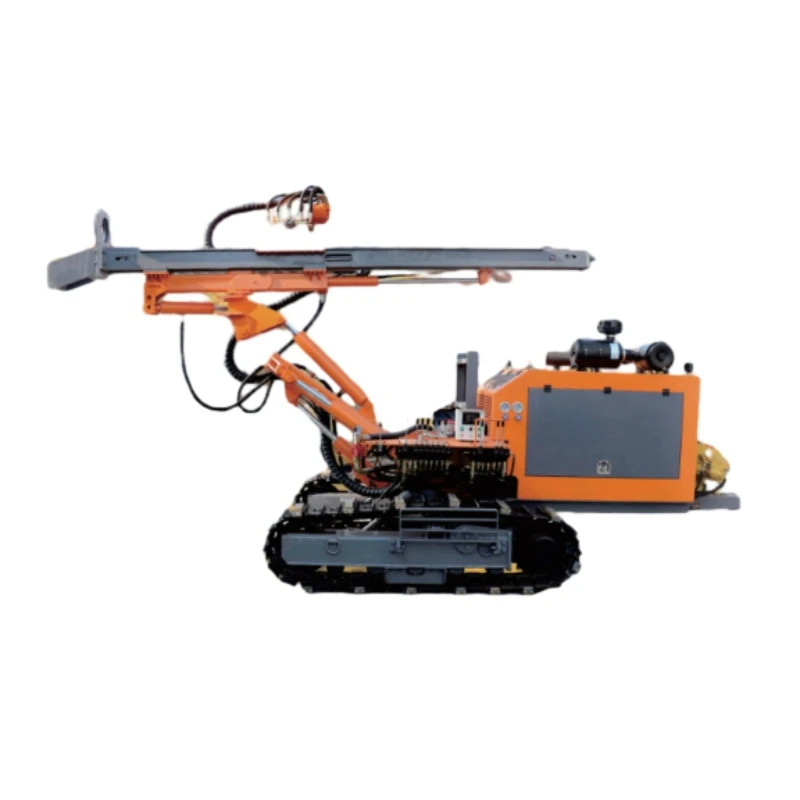
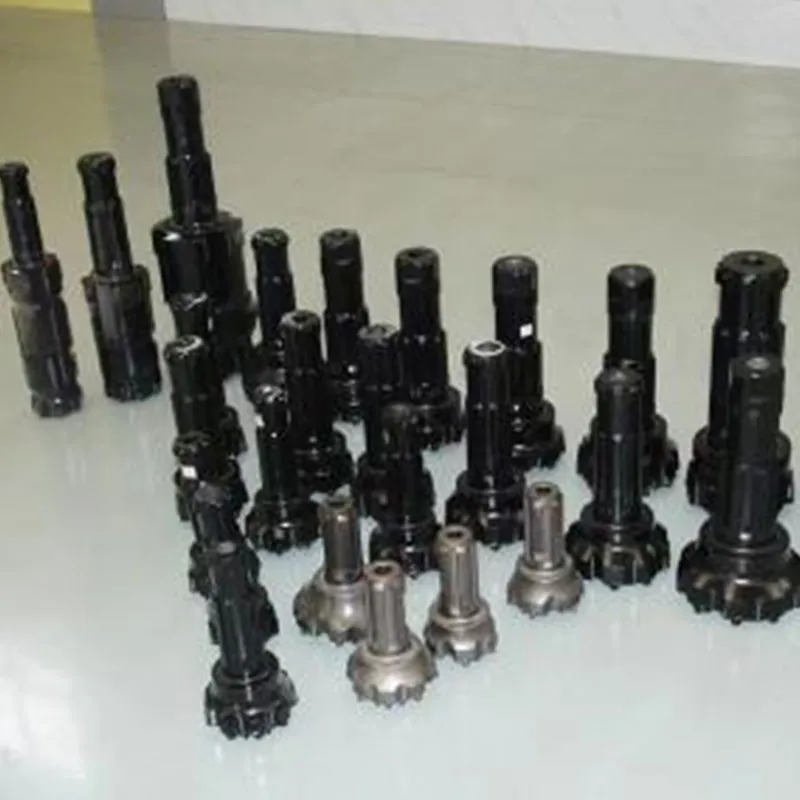


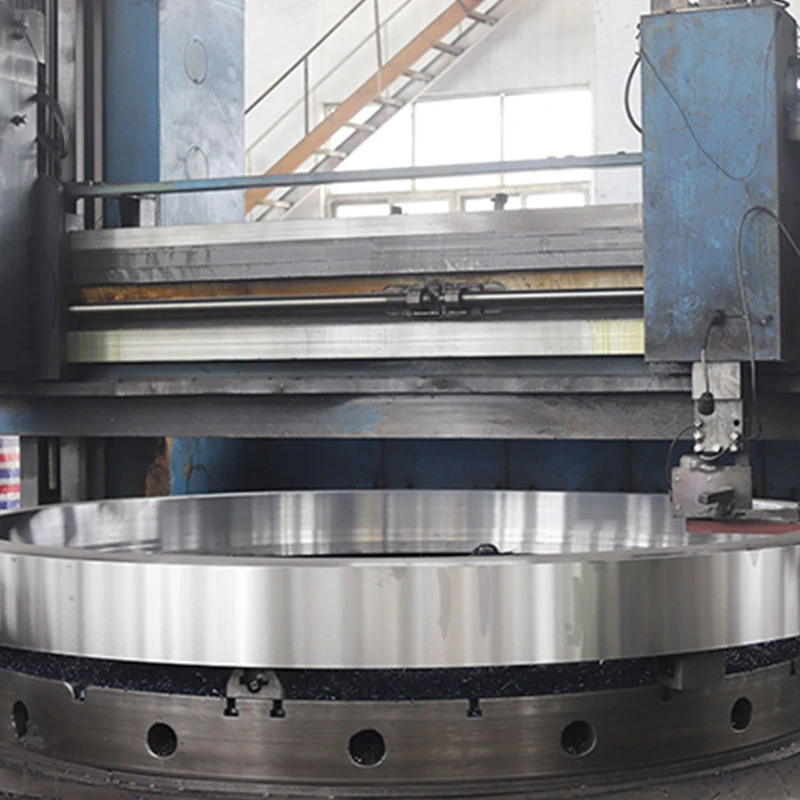
The expertise involved in the design and development of submersible pump shafts is extensive. Engineers must consider dynamic loadings, hydrodynamic forces, and thermal effects throughout the design process. Simulation tools such as Finite Element Analysis (FEA) play an integral role in testing and validating design choices before physical manufacturing, allowing engineers to anticipate potential weaknesses and areas of stress concentration. These analytical techniques have become a standard practice, reinforcing the shafts' ability to withstand the demanding conditions they are subjected to. Authoritativeness in the sector is demonstrated by compliance with international standards and certifications, such as those provided by ISO and ASTM. Adherence to these standards assures stakeholders of the product's quality and safety. Manufacturers with comprehensive certifications often enjoy a competitive edge, as this serves as a testament to their commitment to excellence and industry best practices. Trust in these products is further bolstered by performance guarantees and extended warranties offered by leading manufacturers. Organizations leveraging these advanced submersible pump shafts have reported a range of operational benefits, from enhanced energy efficiency to reduced emissions. Such outcomes are increasingly important in an era where ecological sustainability and cost-effectiveness are pivotal to business strategy and regulatory compliance. In conclusion, the evolution of submersible pump shafts exemplifies the integration of experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness within the product domain. By prioritizing material integrity, precision engineering, and technological integration, the industry continues to drive innovations that meet the modern demands of performance and sustainability. As a result, end users and stakeholders alike can rely on these critical components for dependable and efficient underwater operations.
-
Low-Cost Borehole Drilling Machine for Small-Scale Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Carbide Bullet Teeth for Abrasive Formations: Powering Industrial Drilling Efficiency
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Advantages of Down-the-Hole Drill Bits in Geothermal Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Hole Hammer Use in Water Well Drilling
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of a Mobile Diesel Compressor in Construction
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Diesel Portable Screw Air Compressors
NewsJul.11,2025