- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Bengali
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- French
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- Miao
- Hungarian
- igbo
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Feb . 19, 2025 00:54 Back to list
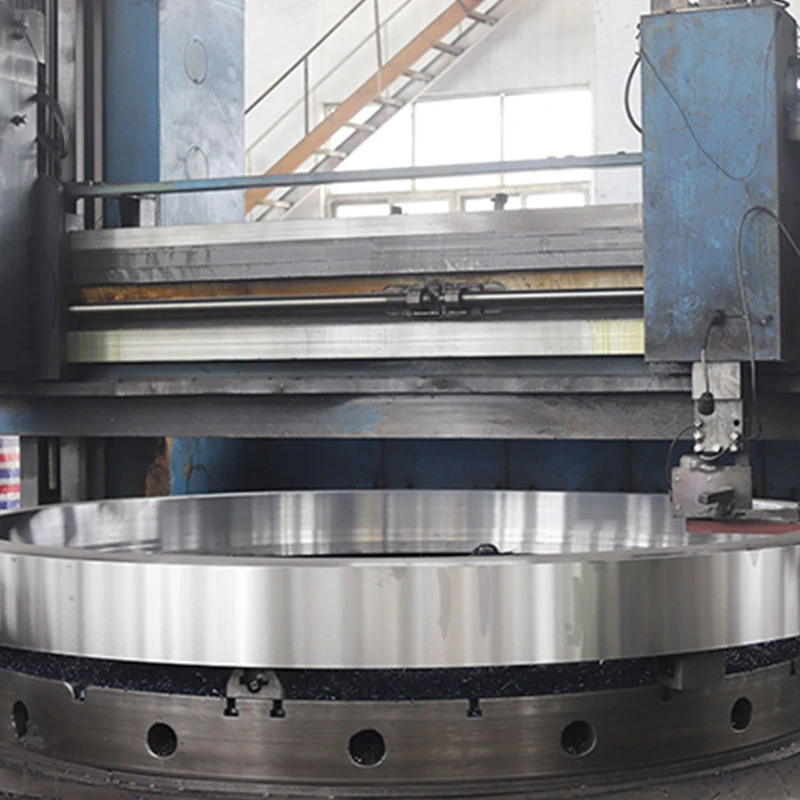
bombas de lodos.


From a technical standpoint, the advancement in materials technology offers new avenues for enhancing mud pump durability and efficiency. The use of high-strength alloys and polymers in pump design has proved effective in combating corrosion and erosion, common challenges faced in abrasive fluid environments. These innovations not only improve pump performance but also foster an environment of safety and reliability across various industries employing these pumps. Moreover, environmental considerations have increasingly become a focal point in pump design and application. Implementing eco-friendly technologies, such as energy-efficient motors and closed-loop systems, not only strengthens compliance with environmental regulations but also bolsters an organization's sustainability credentials. Through the lens of authority and trustworthiness, manufacturers and suppliers of mud pumps invest significantly in research and development to deliver products that meet stringent international standards. Certifications and adherence to guidelines set forth by industry bodies enhance a product's credibility, reassuring end-users of its quality and reliability. In conclusion, understanding and optimizing the use of mud pumps, or bombas de lodos, necessitates a blend of technical know-how, industry-specific insights, and a commitment to sustainability. Employing these pumps effectively ensures operational success across oil, mining, and construction sectors while aligning with broader environmental and economic goals. As technology progresses, the continued evolution of these pumps will undoubtedly drive the industry forward, marking their importance within industrial ecosystems.
-
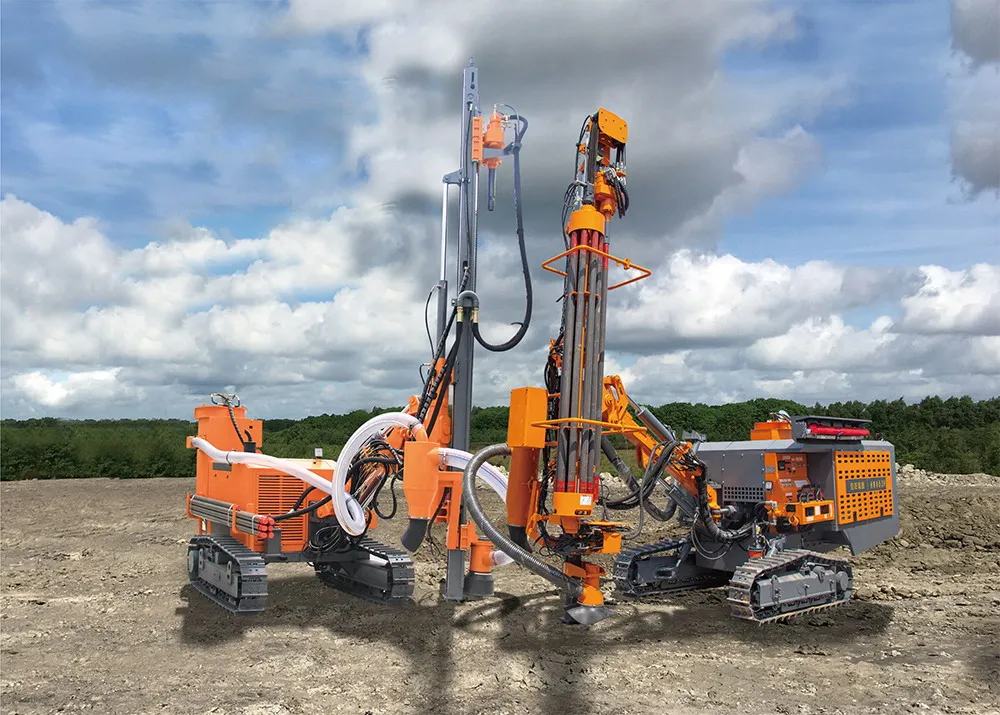
Low-Cost Borehole Drilling Machine for Small-Scale Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Carbide Bullet Teeth for Abrasive Formations: Powering Industrial Drilling Efficiency
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Advantages of Down-the-Hole Drill Bits in Geothermal Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Hole Hammer Use in Water Well Drilling
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of a Mobile Diesel Compressor in Construction
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Diesel Portable Screw Air Compressors
NewsJul.11,2025