- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Bengali
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- French
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- Miao
- Hungarian
- igbo
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Feb . 15, 2025 20:29 Back to list
agujero submarino martillo de agua
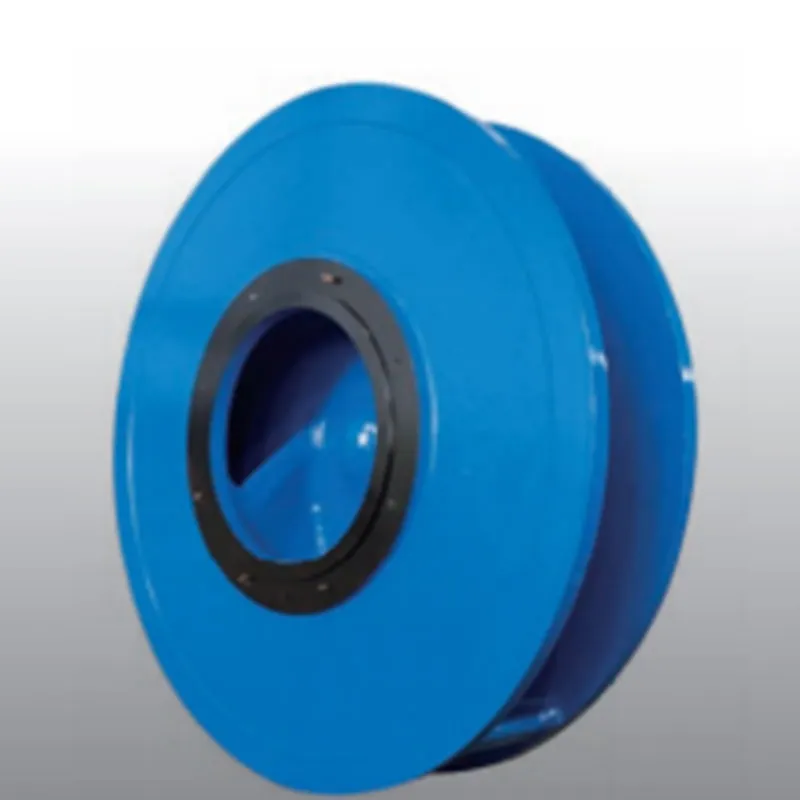
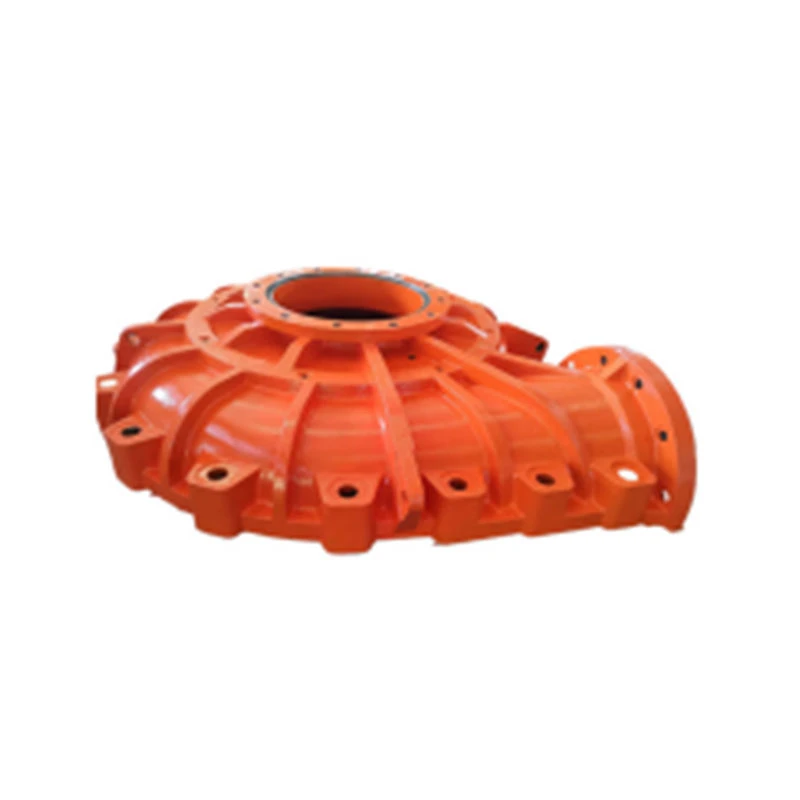


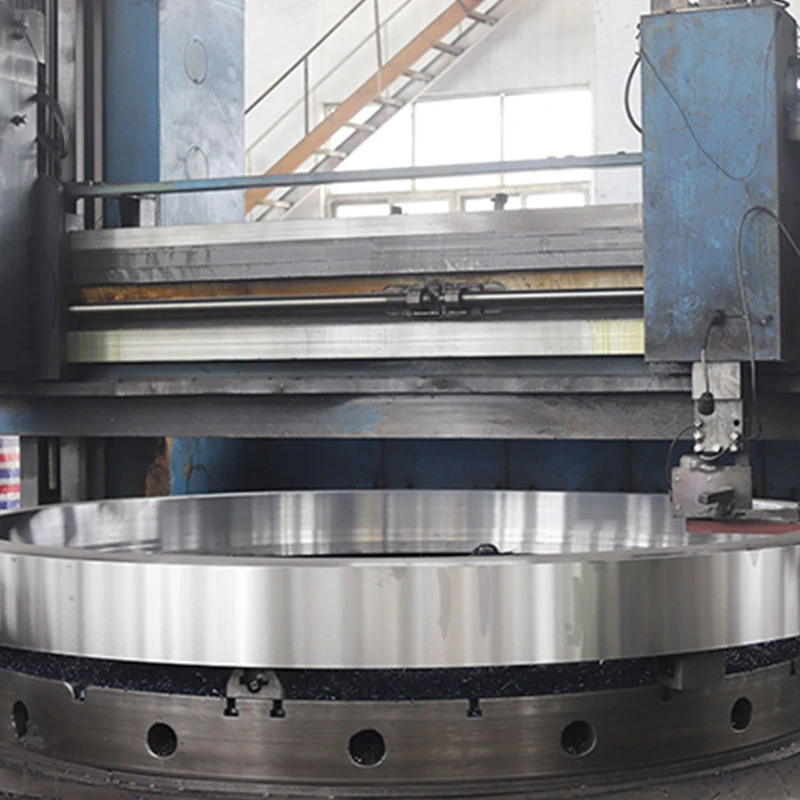
From an expertise standpoint, the implications for underwater engineering and marine physics are profound. Utilizing knowledge from fluid dynamics, engineers have developed advanced materials capable of withstanding intense pressures. Moreover, by understanding these water hammer holes, offshore drilling operations can be adjusted to minimize risks. Companies such as Schlumberger and Halliburton are actively researching how to incorporate these findings to optimize drilling operations and enhance safety protocols. Trust and authority in the field are further reinforced by local and international regulatory bodies, who are beginning to outline guidelines for commercial operations near suspected water hammer zones. Their goal is preserving the delicate ecological balance of our oceans while allowing technological and industrial advancement to continue unimpeded. NOAA and the International Maritime Organization (IMO) play crucial roles in ensuring these guidelines are adhered to, fostering safe and responsible exploration. For product developers in the engineering sectors, particularly those involved in designing submersible technology and undersea construction materials, the implications are vast. Developing new products that can withstand or exploit these unique conditions represents a significant opportunity. Advanced pressure-resistant alloys and sealants are currently under development, promising to revolutionize underwater construction. Lastly, the trustworthiness of information and research surrounding underwater water hammer holes benefits from cross-disciplinary collaboration. Researchers from physics, marine biology, engineering, and environmental science converge, ensuring that findings are robust, reproducible, and applicable across various domains. Peer-reviewed studies and international symposiums provide a platform for sharing insights, fostering an environment of trust and continual learning. In conclusion, the exploration of underwater water hammer holes not only deepens our understanding of marine dynamics but propels advances in technology and industry. With the continued commitment to research and innovation, the mysteries of the ocean's depths may soon offer unprecedented opportunities for exploration and development.
-
Low-Cost Borehole Drilling Machine for Small-Scale Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Carbide Bullet Teeth for Abrasive Formations: Powering Industrial Drilling Efficiency
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Advantages of Down-the-Hole Drill Bits in Geothermal Projects
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Hole Hammer Use in Water Well Drilling
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of a Mobile Diesel Compressor in Construction
NewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Diesel Portable Screw Air Compressors
NewsJul.11,2025