- Aircraft spark plugs are specially designed to withstand the harsh conditions and high temperatures encountered in the engine compartment of an aircraft. They are made of durable materials such as nickel alloy, platinum, or iridium that can withstand extreme heat and pressure. This durability is essential for ensuring the reliable operation of the aircraft engine during flight.
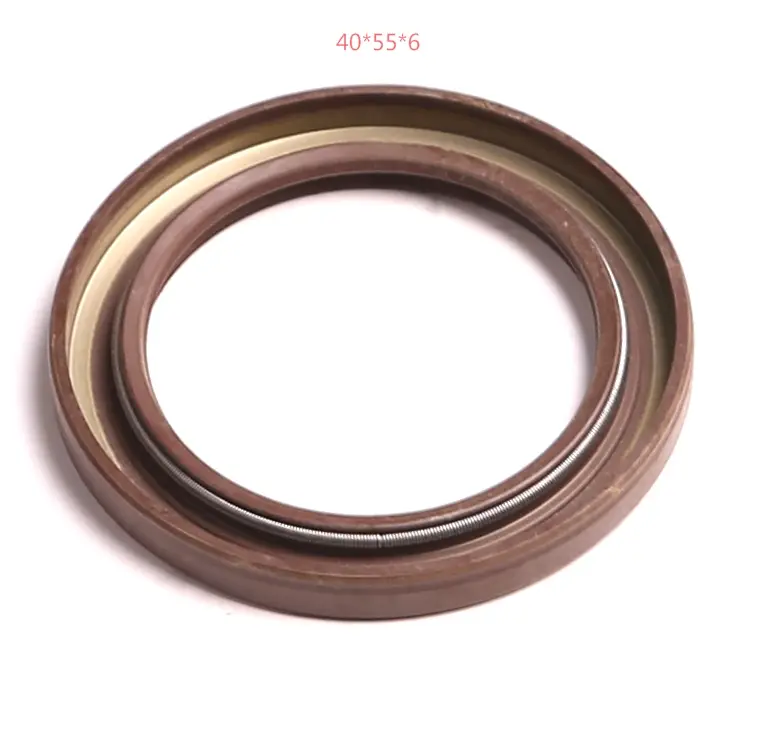
An oil seal is designed to perform three major functions: to prevent lubricants from leaking outside the seal even under high pressure, to act as a barrier to retain the lubricating oil, and to prevent dirt and other contaminants from entering the unit.
 4.6 valve cover gasket. It can also lead to a loss of oil, necessitating more frequent top-ups and potentially causing engine overheating due to inadequate lubrication.
4.6 valve cover gasket. It can also lead to a loss of oil, necessitating more frequent top-ups and potentially causing engine overheating due to inadequate lubrication.
Recognizing and avoiding common installation mistakes is key to the longevity and effectiveness of oil seals. Here are some frequent errors to watch for:
Conventional oil is the most commonly used type of oil. It is ideal for light-duty, late-model cars with low to average mileage and a simple engine design.

thick rubber gasket. This makes them ideal for outdoor and harsh environment applications where other materials may deteriorate quickly. Additionally, rubber gaskets are non-conductive and can provide an effective barrier against electrical currents, reducing the risk of electrical hazards.
■Rust and corrosion inhibitors: Your engine’s internal parts can rust and corrode when exposed to acids and moisture. These additives create a protective film over your engine’s internal parts to help prevent such damage.
 They initiate the combustion process by generating a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber They initiate the combustion process by generating a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber
They initiate the combustion process by generating a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber They initiate the combustion process by generating a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber 794 000 spark plug. A properly functioning spark plug ensures a smooth, efficient burn, translating into better fuel economy, reduced emissions, and increased engine power.
794 000 spark plug. A properly functioning spark plug ensures a smooth, efficient burn, translating into better fuel economy, reduced emissions, and increased engine power.Rotary shaft or oil seals are placed between moving and stationary pieces of machinery to ensure that contaminants, moisture, corrosive materials and abrasives do not damage the various components. They can also prevent unwanted mixing of fluids, including water and oil combining within a machine.
Installing Oil Seals: A Step-by-Step Guide
③
Oil Seals 101 – The Ultimate Guide
Refit all pipes and wires, and the air cleaner. Start the engine and check for oil leaks.
Innovations in Oil Seal Manufacturing: Advancing Performance and Reliability
An oil seal, also known as crankshaft retainer, is a small device, but essential to ensure the proper engine operation. It plays a key role in all moving parts of an engine, acting as a physical barrier. This mechanical seal fulfils the dual purpose of sealing a rotary shaft to maintain the necessary lubrication (avoiding leaks) and preventing other foreign matter from contaminating shafts and bearings in the rotary shaft equipment.